soil food web pdf
Fifth and higher trophic level. The soil fauna and microflora form part of food webs in which they are both consumers and are themselves consumed see Chapter 10.

What Is The Soil Food Web Soil Food Web Diagram Hendrikus Organics
In the soil food web they eat.

. Management practices can change food webs. Trimmings manures and food processing discards go into producing composts. There are millions of soil bacteria in every ounce of soil.
They regulate populations of other soil organisms like protozoa which help maintain a healthy soil food web and control disease-causing organisms. FOOD WEB SOIL HEALTH. Soil food webs are driven by the chemical energy contained in detritus that is harnessed by soil microorganisms.
Responses of microbial components of the rhizosphere to plant management strategies in semiarid rangeland. The cycling of nutrients in the soil is very important as plants depend on them to grow and plants are the producers which provide food for most of the food webs on Earth. For example tillage practices fertiliser and chemical applications can have a negative influence on soil microbial communities while.
A Closer Look at Soil Food Webs 1 Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that can be important decomposers and also act to filter and break down some pollutants. The Soil Food Web. 2 Protozoa are another single-celled microorganism or microbe that eat bacteria.
Similar to the food chains you learned about in grade school the Soil Food Web depicts the interrelationship of organisms within and dependent on your soil and compost. As carbon and energy flow through the soil food web they are depleted by the metabolic and production functions of. Enhance porosity as they move through the soil.
Protozoa or bacterial feeding nematodes are abundant where bacteria are plentiful. Part II then addresses how compost contributes to the soil food web and overall plant health. The soil food web is a concept that helps explain the natural processes constantly active in our soil and their interaction with plant life.
Growing cover crops which photosynthesize at times of the year when grain crops are not growing or active will. In turn soil arthropods are consumed by burrowing mammals birds and lizards. In one teaspoon of soil alone there may be over.
Soil is made up of broken down rock and mineral matter mixed with decomposing organic matter and living organisms. Matter soil arthropods help improve soil structure and change nutrients into forms available to plants. The plants lichens moss photosynthetic.
In the Soil Foodweb everything eats and everything excretes and everything is food for something. The Soil Foodweb is a complex mutually beneficial population of microbes which develop soil structure and release natural nutrients for uptake by plants. Many effects of soil organisms are a result of the interac琀椀漀渀猀 愀洀漀渀最 漀爀最愀渀椀猀洀猀Ⰰ 爀愀琀栀攀爀 琀栀愀渀 琀栀攀 愀挀琀椀漀渀猀 漀昀 椀渀搀椀瘀椀搀甀愀氀 猀瀀攀挀椀攀猀.
Plant and Soil 8565-76. Elaine Ingham PhD has been at the forefront of educating farmers about the value of understanding soil life. Of the Soil Food Web.
Of energy is called a food web. Energy and nutrients are passed through the trophic levels of a food web. The presence of predators in the food web reflects their food source ie.
It is very important to your composting and gardening success that you understand the basics of the Soil Food Web. Soil food webs have producers green plants lichens and. Learning Objective To be able to identify what organisms are producers consumers and decomposers.
There is more life in the ground than above in the ground. Some species make permanent burrows deep into the soil and can be a major conduit for soil drainage particularly. The higher-level predators in the soil food web include.
Nseen beneath our feet there dwells a teeming microscopic universe of complex living organisms that few humans ever consider. I wanted to discuss how this works in an indoor organic growing environment but first a brief discussion of the soil food web. Tuning in to the World Beneath Our Feet by Mary-Howell R.
All food webs are fueled by the primary producers. Agriculture can enhance the soil food web to create more soil life by better utilizing the suns energy. Reprinted from April 2000 - Vol.
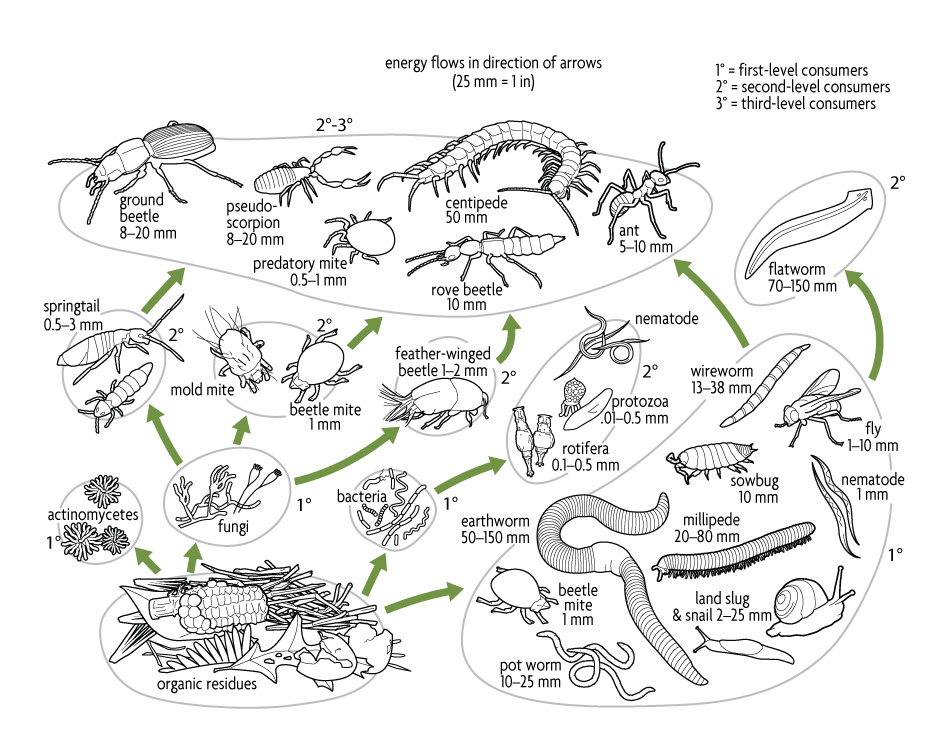
This diagram shows a simplified version of the soil food web with the different organisms that are found in a healthy environment. A food web diagram shows a series of conversions represented by arrows of energy and nutrients as one organism eats another see food web diagram below. Materials used to feed compost microorganisms are referred to as compost feedstocks Part I of this fact sheet addresses the composting process and associated microorganisms.
Agroecological systems to control pests and improve soil health. Energy is transferred between. Food webs identify the relationships among producers consumers and decomposers in an ecosystem.
In particular we study soil ecology plant pest interactions and biological controlboth independently and through collaborations with industry and other laboratories. A food web diagram shows a series of conversions represented by arrows of energy and nutrients as one organism eats another. Healthy soil is flourishing with microorganisms and the complex interactions between the flora and the fauna create a soil food web.
Review of the effects of twelve selected biocides on target and non-target soil organisms. Up to 24 cash back The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. Pest Detection qPCR-Orchard nematodes qPCR-carrot nematodes Cultural Control Amendments - compost food.
The illustration above is known as the Soil Food Web. Food sources that are either living plant tissue or dead organic matter such as plant litter or the dung and dead remains of soil or above-ground organisms. So heres how it works.
Thus the suns energy is converted to higher-level mammals which can be a source of food for humans. A mite feeds on a springtail and releases nutrients into the soil. The soil food web.
THE SOIL FOODWEB. The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. Students consult the field guide at The Dirt on Soil - Learning Adventures and conduct a hands-on exercise.
A large proportion of soil passes through the guts of earthworms and they can turn over the top six inches 15 cm of soil in ten to twenty years. The soil food web Plant residues roots and organic compounds Soil organic matter Basal trophic level.

Dr Elaine S Soil Food Web School Regenerative Agriculture Courses

Trophic Levels And Trophic Efficiency

Food Web Posters Food Chain Activities Food Web Food Chain

Biological Activity Ndsu Soil Health

Below Ground Connections Underlying Above Ground Food Production A Framework For Optimising Ecological Connections In The Rhizosphere Vries 2017 Journal Of Ecology Wiley Online Library

Soil Biota An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Dr Elaine S Soil Food Web School Regenerative Agriculture Courses

Soil Food Web An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Building Structure In Soil Soil Food Web School Youtube

What Is The Soil Food Web Soil Food Web Diagram Hendrikus Organics

Soil Biota An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Food Chain Definition Types Facts Britannica

Food Web Ecology An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Soil Food Web An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Soil Food Web An Overview Sciencedirect Topics